
What is a Webhook? When to Use Webhooks?
What is a Webhook?
A webhook (also known as web callback or HTTP push API) is a way for a system to provide real-time information to other systems. Webhooks deliver data to other systems based on recently occurred events, meaning you receive data immediately without the need for frequent API calls to retrieve real-time data. This makes webhooks much more efficient for both service providers and your system. The only drawback of webhooks is the initial connection setup.
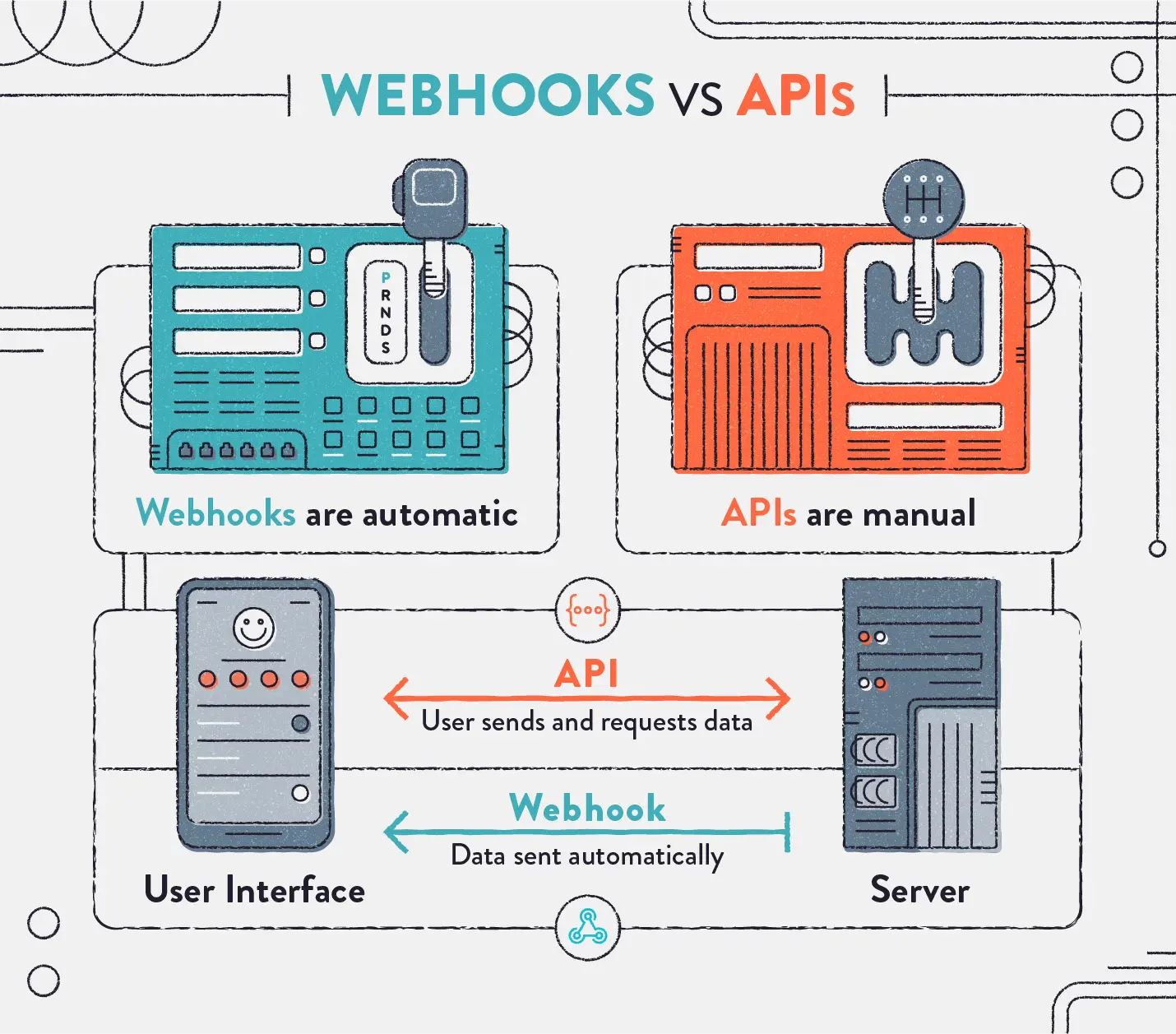
To help visualize, take a look at the image above comparing webhooks to APIs. While webhooks automatically receive data from the server, APIs need to repeatedly send requests to receive data.
Webhooks are sometimes referred to as "Reverse APIs" because they provide you with parameters and you must design an API for the webhook to use. The webhook will make an HTTP request to your application (usually POST) including all those parameters.
Using Webhooks
Typically, you will need to provide a URL to the webhook service provider for them to send requests to. This is usually done through a management page or an API. This also means that you need to implement a URL in your system for the webhook to call.
Most webhooks will send data back to you in either JSON (common) or XML (less common) format. The webhook provider will inform you how they deliver data through their documentation.
When to Use Webhooks?
Webhooks are widely used by major internet platforms and systems. For example, Facebook Page provides webhooks to send events such as user likes, page follows, comments, or even messages to your registered system. Similarly, Zalo provides webhooks to handle similar events on their Zalo Page.
In general, when integrating your system into another system’s infrastructure, webhooks are often the preferred method. So, when implementing integrations, it is likely you will be working with webhooks.
Security
Implementing a URL in your system to provide for webhooks makes it possible for others to find that URL and send malicious requests, causing your system to behave incorrectly. To prevent this, you can employ some security techniques. The easiest way is to provide an HTTPS URL. Additionally, you can consider the following:
- The first and most widely supported approach to securing webhooks is to add a token to the URL, e.g. ?auth=token.
- Another option is to implement Basic Auth, which is also widely used and straightforward to implement.
- The first two solutions effectively prevent most webhook attacks, but they have the disadvantage of having to send authentication credentials with each request. A third option is to require the webhook service provider to sign each request they make to your system and then you verify that signature. This implementation is slightly more complex, and I will make time to write a guide on implementing this approach as a webhook service provider.
Some Considerations
There are a few things to keep in mind when providing your system's URL for use with a webhook service:
- Webhooks deliver data to your system via an HTTP request. This means that if your system encounters errors, the webhook data delivered to you can be lost. Many webhooks will actively retry requests if they detect that your system is experiencing issues. So, be sure to carefully read the webhook service provider's documentation to understand how they handle HTTP requests to your system.
- When events occur continuously, webhooks can make continuous HTTP requests. Make sure your system can handle this in its implementation.
Recap
Webhooks provide a way for a system to deliver real-time information to other systems, eliminating the need for frequent API calls. Most webhooks operate based on events to notify registered systems by making an HTTP request.
Currently, most major Internet service platforms provide webhooks for easy integration with your application system. Additionally, attention should be paid to the security and implementation of webhooks.
References:
The secret stack of Blog
As a developer, are you curious about the technology secrets or the technical debts of this blog? All secrets will be revealed in the article below. What are you waiting for, click now!
Subscribe to receive new article notifications
Comments (2)
Không cmt bằng hình ảnh được nhỉ
Không cmt bằng hình ảnh được nhỉ
Ad ơi bị lỗi giao diện trên mobile rồi kìa :))
Ad ơi bị lỗi giao diện trên mobile rồi kìa :))
Ok bạn ơi mình thấy rồi, thanks b
Đã fix rồi nha bạn