
What is a Functor? Do I need to know about functors?
Issue
The concept of Functor is a stepping stone to discover new things in the world of functional programming. So what is a functor and what benefits does it bring to programming?
What is a Functor?
In essence, a functor is a data structure that you can map over to apply a function to each element for the purpose of modifying the data. However, an important point to note is that this data is contained within a "container", so in order to modify the value, the functions must extract it, modify it, and put the value back into the "container".
A functor is also called a fmap. Here is the general definition of fmap:
fmap :: (A -> B) -> Wrapper(A) -> Wrapper(B)
The fmap function takes a function (A -> B) and transforms the function Wrapper(A) into Wrapper(B) after transforming the values A into B. To understand this more clearly, you can refer to the diagram below:
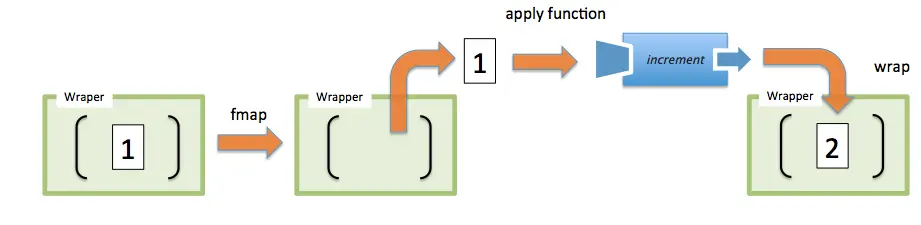
We can see that the value 1 is extracted from the "container" -> the function is applied -> the value is put back into the "container".
Basically, fmap returns a new copy of the "container" each time it is called, so it can be considered immutable.
That's the theory, let me give you a specific example: Representing the calculation 2 + 3 = 5 using functors.
First, I will build a Wrapper class that takes a value, this class has two methods: fmap for transformation and identity to extract the value:
class Wrapper {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
}
fmap(fn) {
return new Wrapper(fn(this.value));
}
identity() {
return this.value;
}
map(fn) {
return fn(this.value);
}
}
fmap takes a function, uses the function to transform the value, and puts it back into the Wrapper. identity simply returns the value.
I will use a curry function to perform addition. If you don't know about curry, you can read the post What is a Curry Function? A delicious "curry" dish and how to enjoy it?.
const plus = a => b => a + b;
const plus3 = plus(3);
const two = new Wrapper(2);
const sum = two.fmap(plus3); // Wrapper(5)
sum.identity(); // 5
By now, can you notice something interesting? That's right, the sum can still continue to use the fmap function, or in other words, when the processing result returns an object as a Wrapper, we don't have to worry about the continuity of the data after processing. I can continue adding, subtracting, multiplying, etc., in a continuous manner:
const multi = a => b => a * b;
const multi5 = multi(5);
sum.fmap(multi5).identity(); // 25
When the result of the fmap function is a Wrapper, it ensures that the result still has the properties of a Wrapper.
Isn't it interesting? Does the idea of a chain of functions remind you of the map or filter functions in JavaScript? Indeed, they are implementations of functors.
map :: (A -> B) -> Array(A) -> Array(B)
filter :: (A -> Boolean) -> Array(A) -> Array(A)
map and filter are considered functors because they have the characteristics of functors:
- Similarity
- Maintaining the structure
- Type-preserving
Functors need to ensure some important properties:
No side effects: You can fmap over an identity function to get the same value in a context. This proves that they do not have side effects and still preserve the structure of the wrapped value. You can think of identity as a function that simply returns the value it receives.
Wrapper('Get Functional').fmap(x => x); // Wrapper('Get Functional')
Secondly, they must be composable. That means they can be fmaped continuously.
To ensure this, the control structures such as fmap must not throw exceptions, change elements in the list, or change the behavior of a function. The aim is to create a context that allows you to manipulate values without changing the original value. This is clearly demonstrated in how the map function transforms this array into another array without modifying the original array.
However, in programming, we don't always have perfect data, and we still have to deal with exceptions, values like null, undefined, etc. At this point, applying functors may not be perfect anymore.
const div = a => b => b/a;
const subtr = a => b => a - b;
const plus = a => b => a + b;
const divided5 = div(5);
const subtr2 = subtr(2);
const plus3 = plus(3);
const two = Wrapper(2);
two.fmap(subtr2).fmap(divided5).fmap(plus3); // Wrapper(NaN)
Conclusion
A functor is a data structure that stores data within a "container" and provides methods to manipulate the data within that "container". By using functors, we ensure that the output of the data will not change in type, similar to how the map function takes an array and always returns an array.
The secret stack of Blog
As a developer, are you curious about the technology secrets or the technical debts of this blog? All secrets will be revealed in the article below. What are you waiting for, click now!
Subscribe to receive new article notifications
Comments (2)
Làm về monad, applicative, monoid chưa ạ?
Làm về monad, applicative, monoid chưa ạ?
Chào bạn, cảm ơn bạn đã theo dõi mình suốt thời gian qua. Hiện tại mình vẫn đang bận rộn với những kế hoạch đề ra từ trước nên trước mắt vẫn chưa hoàn thành bài viết này được. Mong bạn thông cảm và tiếp tục ủng hộ :D
Làm về monad, applicative, monoid đi ạ
Làm về monad, applicative, monoid đi ạ
Hi bạn, mình cũng đang trong quá trình tìm hiểu về lập trình hàm thôi nên nếu cảm thấy đủ hiểu thì mình sẽ viết các bài chi tiết
Làm về monad, applicative, monoid có chưa ạ