
Are browsers no longer able to run C/C++, Go... JavaScript?
Issues
I used to wonder if browsers could run languages other than JavaScript, such as Python or Golang. Because we all know that JavaScript has been the dominant language in browsers for a long time, it is the primary language for interacting with browser components.
JavaScript is powerful, but it also has its drawbacks. It consumes a lot of memory and can struggle with heavy computational tasks, causing the main thread to freeze and making user interactions with web pages terrible.
Nowadays, as user experiences have evolved, especially with the emergence of VR and NFT applications, websites need to handle more. JavaScript is currently able to handle this, but it is time for us to have new tools to support it.
Introduction to WebAssembly
What is WebAssembly?
WebAssembly (WASM) is a binary instruction format that runs in browsers or on servers. It is designed for performance and security. WebAssembly can be compiled from other programming languages such as C/C++, C#, Rust, Go, and many others.
What can WebAssembly do?
WebAssembly is used to execute heavy and computationally intensive tasks of web applications. This allows JavaScript to focus on handling the interactive aspects of the browser while letting WebAssembly handle the heavy lifting. WASM was initially created for the web, and it has many use cases such as image/video editing, gaming, VR, simulation on the web platform, and more.
Will WebAssembly replace JavaScript?
No! Or at least, it cannot replace JavaScript yet. As mentioned earlier, WebAssembly replaces JavaScript for CPU-intensive tasks, but JavaScript still cannot be replaced for user interaction.
The future of WebAssembly
Although WASM is still relatively new, with the development of current websites, the search for an optimization tool, WASM is becoming a promising candidate. WASM has been and is being used by applications like AutoCad and Figma for a long time. Let's look forward to the future advancements of WebAssembly.
Using WebAssembly
WebAssembly supports various programming languages. You can see a list at https://webassembly.org/getting-started/developers-guide/.
To use WebAssembly, the code of other programming languages is compiled into the binary format with the .wasm extension. Then, import the file into HTML code and start using the modules you have written. The following example demonstrates how to write a module in Go and use it with WebAssembly.
First, create a file named hello.go with a simple main function that prints "Hello, WebAssembly":
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Println("Hello, WebAssembly!")
}
Then, build the file into the .wasm format for browser usage:
$ GOOS=js GOARCH=wasm go build -o main.wasm
To run the .wasm file in the browser, you need to use a .js file for support. For Golang, you can find it at:
$ cp "$(go env GOROOT)/misc/wasm/wasm_exec.js" .
Now, create an index.html file to use wasm:
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<script src="wasm_exec.js"></script>
<script>
const go = new Go();
WebAssembly.instantiateStreaming(fetch("main.wasm"), go.importObject).then((result) => {
go.run(result.instance);
});
</script>
</head>
<body></body>
</html>
Then, run an HTTP server. Here, I will use the http-server package:
$ http-server .
Access http://127.0.0.1:8080 in your browser, and you will see "Hello, WebAssembly!" printed in the console.
Let's add a function to calculate the sum of two numbers in Golang and call it from JavaScript:
package main
import "syscall/js"
func main() {
js.Global().Set("wasmAdd", js.FuncOf(add))
<-make(chan bool)
}
func add(this js.Value, args []js.Value) interface{} {
return args[0].Int() + args[1].Int()
}
syscall/js is the Go library that supports WebAssembly. I created an add function that returns the sum of two parameters.js.Global().Set("wasmAdd", js.FuncOf(add)) is used to set the Go add function as the wasmAdd function to be used in JavaScript.<-make(chan bool) prevents the Go program from exiting when it finishes executing.
Now, recompile the .wasm module using the steps above. Refresh the browser, and from the console window, call the wasmAdd(1,2) function:
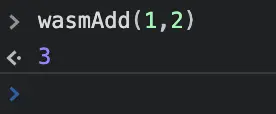
It's that simple, isn't it!
Conclusion
WebAssembly is a portable binary instruction format that runs in browsers or on servers. WebAssembly can be compiled from other programming languages such as C/C++, C#, Rust, Go, and many others.
WebAssembly is used to execute heavy and computationally intensive tasks of web applications. It was not created to replace JavaScript.
Me & the desire to "play with words"
Have you tried writing? And then failed or not satisfied? At 2coffee.dev we have had a hard time with writing. Don't be discouraged, because now we have a way to help you. Click to become a member now!
Subscribe to receive new article notifications
Comments (3)
Assem vẫn còn chưa phổ biến lắm
Assem vẫn còn chưa phổ biến lắm
Có hướng dẫn với python không ah?
Có hướng dẫn với python không ah?
Hiện tại có vẻ như Python vẫn chưa chính thức hỗ trợ cho ưebassembly. Tuy nhiên có một số thư viện không chính thức đã được phát hành bạn có thể tìm hiểu thêm xem sao!
Bạn ra thêm bài viết về webassembly đi mình cũng đang tìm hiểu cái này
Bạn ra thêm bài viết về webassembly đi mình cũng đang tìm hiểu cái này
B cần tìm hiểu thêm gì mình sẽ nghiên cứu thêm